Doors.NET - Personal and Corporate Firewalls
1.0 Personal Firewalls
A personal firewall is a consumer software application for the PC user that usually resides on the machine being protected. The user is the administrator of this application and can change firewall configuration and settings. Unfortunately, these programs can sometimes be difficult to configure and configuring of third-party firewall applications is beyond the scope of this help file (due to the many variations that are available). The general principle, however is that Doors.NET needs to be added to the exceptions list as an allowed application.
Many versions of Windows operating system have the personal firewall turned on by default, you will therefore need to add the Doors.NET client.exe to the list of allowed programs. To do this, follow the steps outlined below:
- Open Control Panel via the start menu.
- Double-click the Windows Firewall icon from the list of Control Panel Items.
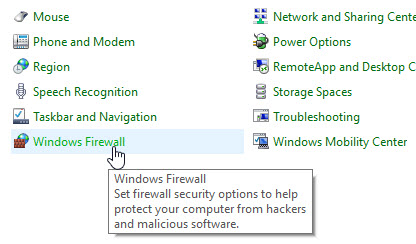
- Click 'Allow and app or feature through Windows Firewall'.
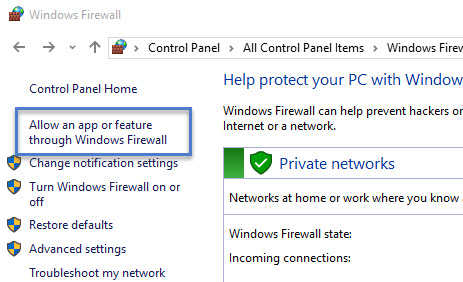
- Click the Exceptions tab or Allow another app...
- Click the Browse button then navigate to C:\Keri\DoorsNET\EclipseServer.exe
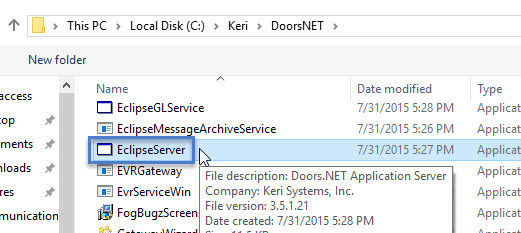
- Click the Add button.
- You will then see the Doors.NET Application Server added to the list of exceptions.
- Click the OK button
- Close out of Control Panel
2.0 Network or Corporate Firewalls
A Network or Corporate Firewall is usually in a work environment with an intranet that allows access to the wider Internet. This firewall prevents outsiders from accessing the network's private data, while also controlling what its own users have access to. A corporate firewall is often installed in a specially designated computer separate from the rest of the network so that no incoming request can get directly at private network resources. Only your Network Administrator can control configuration changes to the firewall. If you need to resolve connection issues in this type of environment, your network administrator will need to assist you.
By default, the following ports are used by the Doors.NET software:
- TCP 11000 (login) - Additional client logins use 11001, 11002, 11003, etc
- TCP 12000 - 120015
If you are trying to access the Application Server across the Internet, then you will need to configure your router/firewall to allow the correct port range and forward the traffic on the port to the Application Server machine's IP address.
Depending on the hardware/controller type you are using there are other communication ports that the system uses (use Port Information link below).
Related Articles
Doors.NET Data Sheet
Doors.NET Data Sheet (attached)Doors.NET System Capacities
This document provides a features and capacities comparison between the Basic, Corporate and Elite versions of Doors.NET. The Basic version of Doors.NET is free-of-charge. There is a charge for the Corporate and Elite versions. The second table ...Doors.NET - Software Update
1.0 Introduction The following guide explains how to update the Doors.NET software and if you are using Visual Doors that will also be updated. Software upgrades are automatically handled by the installation program. The installation program ...Doors.NET - End User's Guide
Doors.NET user guide for the end-users (attached).Doors.NET - End Users Guide
Doors.NET End Users Guide (attached)